
In a world where digital threats are growing faster than ever, your SAP landscape isn’t just a business tool — it’s a target. Whether you’re opening connections for remote support, linking systems across your enterprise, or interacting with third-party vendors, every access point is a potential vulnerability.
That’s where SAProuter comes in — your first line of defense and smart traffic controller. In this post, we’ll break down what SAProuter does, why it’s essential, and how to secure it effectively in today’s high-risk IT climate.
Content
- What Is SAProuter and Why It’s Essential for SAP Network Security
- Top Use Cases of SAProuter
- SAProuter Requirements: What You Need Before Installation
- Step-by-Step Guide to Installing and Configuring SAProuter Securely
- How SAProuter Works: Behind the Scenes of SAP Network Routing
- Why SAProuter Security Matters: Protecting the Gateway to Your SAP Systems
- Key Takeaways and next Steps
What Is SAProuter and Why It’s Essential for SAP Network Security
SAProuter is a standalone software application designed to protect your SAP network from unauthorized access. It acts as a proxy, managing network connections between SAP systems or between SAP systems and external networks. SAProuter enhances the security of your existing firewall by adding an extra layer of protection.
SAProuter is installed on the firewall host and operates through a designated port, which serves as a gateway to your firewall-protected system.
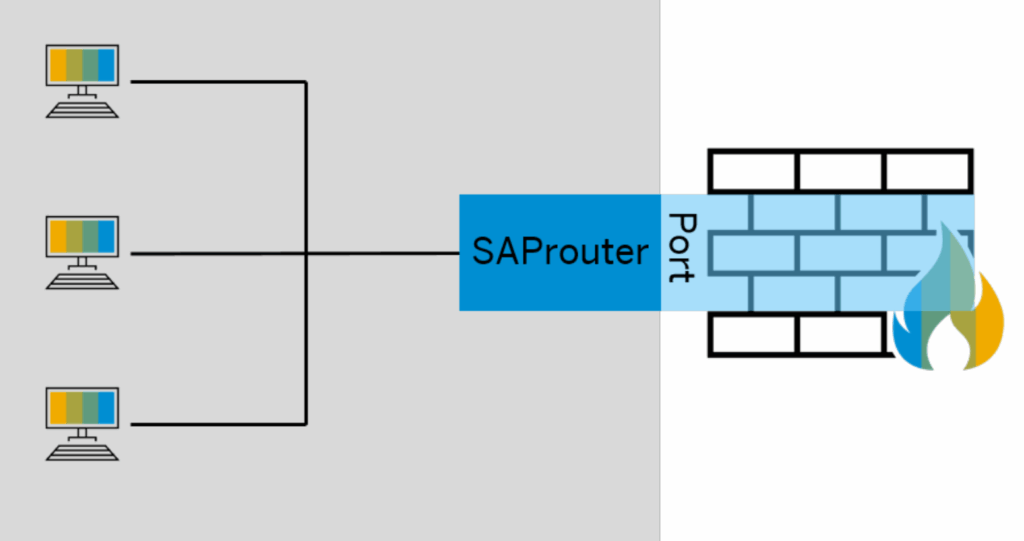
Placing SAProuter in a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) enhances network segmentation by isolating external access points from the internal SAP environment. The firewall governs access to the DMZ, while SAProuter applies strict routing rules defined in its Route Permission Table to permit only authorized connections. This multi-layered architecture minimizes the attack surface and enforces granular control over SAP communication paths.
Top Use Cases of SAProuter
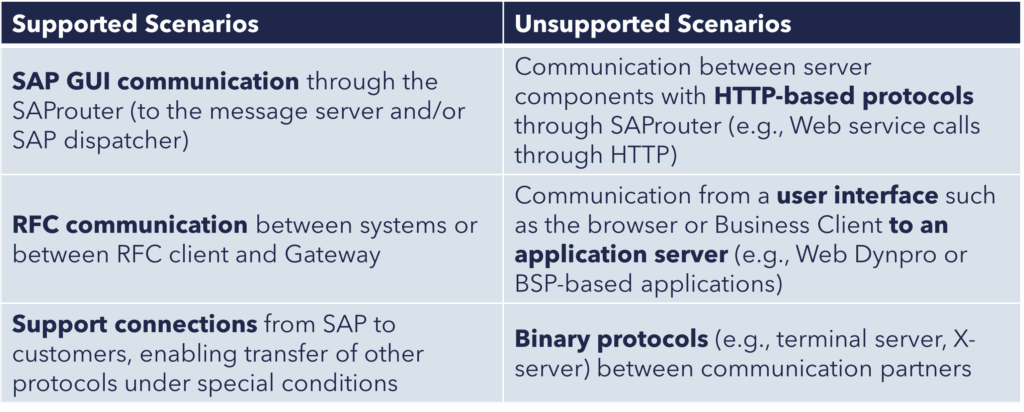
While SAProuter offers a range of powerful use cases that improve security, connectivity, and performance across SAP environments, it’s important to understand its intended scope. Not every communication scenario is compatible with SAProuter. In the table below, we’ll look at which scenarios are supported (and where SAProuter should not be used) to ensure proper implementation and avoid unexpected connectivity issues.
SAProuter Requirements: What You Need Before Installation
The primary prerequisite for using SAProuter is a network connection between the customer’s network and the SAP network. To establish this connection, coordination with the SAP network team is required to prepare your environment.
To ensure a smooth process, please make sure the following steps are taken:
New Connection Requirements
- Before logging a ticket for SAProuter network configuration, you must have or be able to provide a contact with basic knowledge of the operating system. While network experience is not required, you should have an internal contact who can assist if necessary.
- To establish your VPN, you will need access to the SAProuter host, which may require assistance from your IPSEC administrator.
- For IPSEC, ensure that two public IP addresses are available.
- Lastly, SAP Note 28976 must be completed to register your new SAProuter installation.
Existing Connection Requirements
- Someone on your team must be able to log into the SAProuter.
- Access to the hardware for the physical connection to SAP is required.
- Additionally, your network administrator will need to log into the SAProuter host.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing and Configuring SAProuter Securely
To install SAProuter, follow the comprehensive steps outlined in the official SAP Developer Guide. This guide provides detailed instructions for downloading, installing and configuring SAProuter on various operating systems.
How SAProuter Works: Behind the Scenes of SAP Network Routing
When a connection request is made, for example by a user or another SAP system, it does not directly reach the destination system. Instead, the request is routed through SAProuter, which uses a set of predefined rules stored in the Route Permission Table file to determine whether the request is permitted.
These rules specify which source IP addresses can communicate with which destination addresses and ports. If the request complies with the rules, SAProuter forwards it to the next point in the connection path. If it does not comply, the request is blocked and the connection is denied.
The path that a request follows is defined using a routing string. This string outlines the sequence of hosts and ports the communication must pass through, which may include multiple SAProuters. SAProuter itself does not interpret or modify the data being transferred; it simply forwards the traffic according to the routing string and access rules.
A route string for a standard entry has following syntax (P=Permit, S=Secure, D=Deny):
<P/S/D <source-host> <dest-host> <dest-serv> <password>
In addition to access control, SAProuter supports encrypted communication. It can use encryption mechanism or rely on Secure Network Communication (SNC) to ensure that data exchanged between systems remains confidential and secure. This is particularly important in support scenarios.
Why SAProuter Security Matters: Protecting the Gateway to Your SAP Systems
Protecting SAProuter is essential because it functions as a key communication bridge between internal SAP systems and external networks. If left unsecured, it can become an entry point for attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive SAP environments. Since SAProuter enables communication across potentially untrusted networks, it plays a critical role in the overall security of any SAP landscape.
Its placement at the intersection of internal systems and external access makes it a high-value target, and therefore, it must be considered an integral part of an organization’s broader security architecture. Incorporating SAProuter into real-time monitoring, vulnerability management, and applying security best practices helps mitigate risks and maintain system integrity.
With our smarterSec Security Platform (SSP) we offer great visibility into SAProuter-specific vulnerabilities and threats, enabling proactive defense measures and better protection of SAP infrastructure.
Key Takeaways and next Steps
SAProuter is an essential tool for businesses leveraging SAP systems. It ensures secure communication between SAP systems and external networks, offering several features like encrypted data transmission, access control, simplified network configuration, and transparent routing. Implementing SAProuter significantly enhance security, streamline system maintenance, and improve performance by optimizing communication paths.
As companies continue to integrate SAP into their business processes, understanding the role and capabilities of SAProuter is critical to maintaining robust security and ensuring seamless communication between SAP systems and external networks.
By utilizing our smarterSec Security Platform (SSP), it is an important step to further strengthen your security, ensuring that your SAP infrastructure remains efficient and compliant with industry standards.