
In SAP ABAP, authorization objects are the silent guardians of your system, and S_DBG is the secret star. Why? It controls access to the ABAP Debugger, your backstage pass to the system’s inner workings. With debugging power, you can pause programs, peek into variables, and influence execution logic on the fly. This is useful for analyzing problems in your program code, but it’s also dangerous if it falls into the wrong hands.
That’s why S_DBG isn’t just a technical checkbox – it’s a security gatekeeper. In today’s compliance driven world, managing this critical authorization object can mean the difference between a secure system and a costly breach.
What is S_DBG?
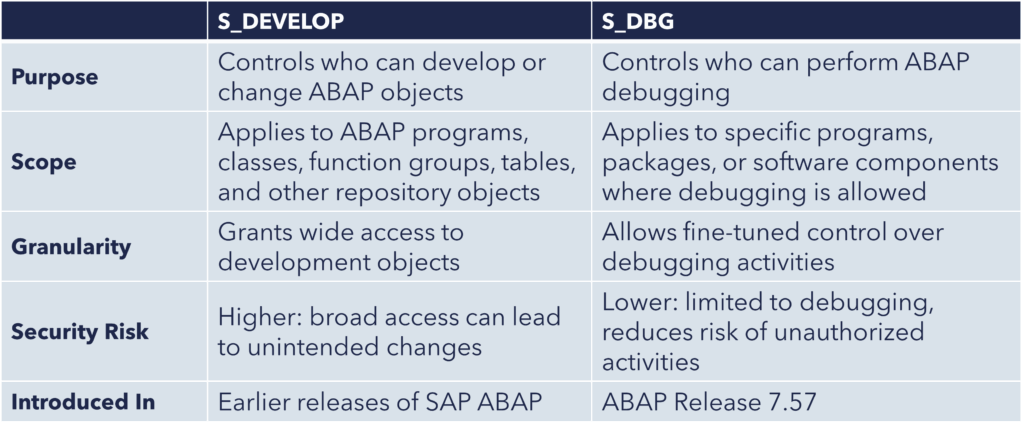
Introduced in ABAP Release 7.57 (2022), the authorization object S_DBG was designed to provide fine-grained control over who can debug what and under which conditions, a capability that its predecessor, S_DEVELOP, did not offer. For many years, S_DEVELOP was the comprehensive solution for development and debugging privileges. As SAP systems grew more complex and security demands tightened, a more specialized approach became essential.
S_DBG is designed to address these demands. While S_DEVELOP still governs a broad spectrum of development and change activities, S_DBG gives administrators a scalpel instead of a hammer. It allows them to fine-tune debugging rights based on software components, packages, and specific actions. In short, it’s the difference between “all access” and “just what you need.”
S_DEVELOP vs S_DBG
While S_DEVELOP and S_DBG may appear similar at first, making an uninformed choice can silently open the door to unintended debugging privileges.
Authorization fields of S_DEVELOP
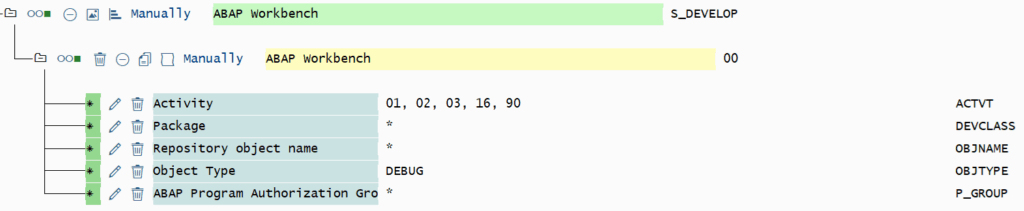
- DEBUG/01: Authorization for debugging the SAP kernel (SAP internal only)
- DEBUG/02: Authorization to change in the debugger
- DEBUG/03: Normal authorization for debugging (start debugger, step by step execution, display field values)
- DEBUG/16: Authorization to execute a debugger script that must be stored in OBJNAME. ACTVT 02 overwrites this activity and generally authorizes the execution of all debugger scripts.
- DEBUG/90: Authorization for debugging remote requests (for example, RFC or HTTP) of another user. Here, the field OBJNAME must be filled with the user name and the field P_GROUP with the client.
Authorization fields of S_DBG
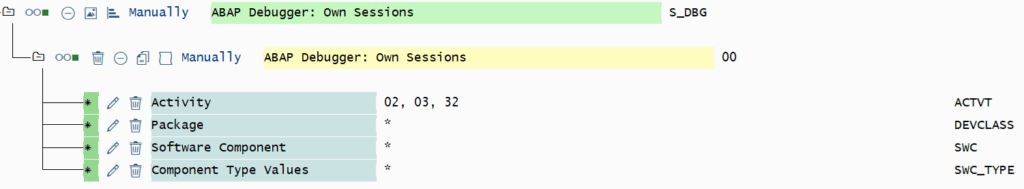
Same authorization fields as in S_DEVELOP:
- ACTVT:
- 02 (Change): Authorization to change variable contents and to jump to a any statement
- 03 (Display): Authorization to debug only (no changes allowed)
- 32 (Save): Authorization to execute database operations (COMMIT/ROLLBACK WORK)
- DEVCLASS: Specifies the development packages
New authorization fields available only for S_DBG:
- SWC: Specifies the software components
- SWC_TYPE: Specifies the type of the software component
Why use S_DBG?
The ABAP Debugger is one of the most powerful tools in the SAP developer’s toolkit. It lets users examine and modify program execution, variables, and logic in real time. However, this power also creates security and compliance risks if not controlled properly. That’s where S_DBG provides the following advantages:
Limitations of S_DBG
While S_DBG marks a significant leap forward in SAP authorization control, it’s important to understand its current boundaries. As of ABAP Release 7.57, S_DBG does not yet offer every debugging functionality that S_DEVELOP provided:
- Remote Debugging: Debugging requests initiated from external systems or remote function calls are not governed by S_DBG.
- Debugger Scripts Execution: Users can still run debugger scripts without S_DBG restrictions, which may pose a risk if not monitored.
- Kernel Debugging: Deep-level debugging within the SAP kernel remains outside the scope of S_DBG and is typically reserved for SAP internal use.
Conclusion
S_DBG empowers SAP administrators to enforce precise debugging controls, reducing risk and enhancing compliance in complex ABAP environments. Yet, implementing and managing this level of granularity requires more than just technical know-how it demands strategic oversight and continuous monitoring.
This is where smarterSec becomes a valuable partner.
By combining deep SAP expertise with targeted security solutions, smarterSec gives you full insight into your SAP landscape. From optimizing role design to ongoing monitoring by the smarterSec Security Platform (SSP), we ensure your SAP systems are not only secure but also scalable and audit-ready.
References and further blogs: